Table of Contents
Ensuring Your Research Stays Visible and General Tips
In the previous lesson of this series, we learned how to plan your next steps when things don’t work out. After dealing with frustrations, rejections, and criticism multiple times, when your paper finally gets accepted, the feeling of joy and sense of achievement is unparalleled. Often this sense of achievement translates to the end of your long research journey.

However, with so many papers being published now and then, it is important to concentrate on improving your research’s visibility. Visible research will eventually lead to more citations and better opportunities (talks, collaboration, employment, higher studies) for its authors.
Through this lesson, I will share the to-do list we follow in our Lab1055 to ensure the visibility of our research.
In this tutorial, you will learn to ensure that your research stays visible.
This lesson is the last in a 5-part series on How to Publish Novel Research:
- Choosing the Research Topic and Reading Its Literature
- Ideating the Solution and Planning Experiments
- Planning and Writing a Research Paper
- Planning Next Steps When Things Don’t Work Out
- Ensuring Your Research Stays Visible and General Tips (this tutorial)
To learn how to ensure your research stays visible, just keep reading.
Ensuring Your Research Stays Visible and General Tips
Below is a to-do list you can follow to ensure your research stays visible. Not everything needs to be done immediately, but going through them in an organized manner can greatly improve the chances of high visibility for the work.
Camera Ready and Acknowledgments
The first task you should do as soon as the paper is accepted is to prepare the camera-ready version. Ensure that the authors’ order, affiliations, and email addresses are correct and current. Next, work on incorporating the reviewers’ and metareviewers’ feedback as things are fresh. The camera-ready version should not differ significantly from the reviewed and accepted version. It’s a good idea to provide the link to the codebase. If you need time to organize and verify the code, provide the link to the empty GitHub repository where it will be uploaded in the future.
Ensure that you talk to your advisor, get the acknowledgments and mention them in the main paper. This can be a separate section at the end (after the conclusion and before references) or the last few lines of the last page. Use this opportunity to thank funding sources, fellowship sources, and labmates who helped with the paper and could not be included as co-authors. You can use the following template for the acknowledgments section.
“This work has been supported by the funding received by _______________. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable feedback that improved the presentation of this paper. We also are grateful to XYZ for insightful discussions on this work.”
Figure 1 provides a few more templates on how to write acknowledgments.

Open Source (arXiv, GitHub, and Project Page)
As soon as you are done with the camera-ready version, upload the same on arXiv. Mention the venue where the work has been accepted (increases the work’s credibility) and the link to the project page or codebase.
The codebase should be clean and should follow a proper file structure. The ReadMe file should start with the work’s title, authors, conference, abstract, and the main figure. Then, it should describe the hardware (number of GPUs, RAM, processor, etc.) and libraries required to reproduce the results in the paper. The good idea is to provide a “requirements.txt” file which can be used with “pip install” to install the exact versions of libraries as used in the code.
Next, it should provide scripts and links to download and set up datasets and run training and inference code. Use configuration files (.yml or .json or .py) to run the exact experiments described in the paper. Finally, end the ReadMe with the BibTeX bibliography.
Another thing you can do to increase the chances of citations is to release the pre-trained checkpoints (via Torch Hub, Google Drive, or Dropbox) of your network and provide a Google Colab tutorial on how to load them and make the inference. This is particularly useful for those looking to use your models off the shelf.
Additionally, create a project page (Figure 2) that summarizes the work’s main idea with sample results and links to the arXiv page and code. Once again, this improves the chances that someone will build upon the work.

Social Media
Using social media, you can increase the reach of your work by several folds. It’s a great idea to announce the research on social media platforms where you are comfortable (e.g., website, Twitter, LinkedIn, etc.). If you are not inclined toward any particular platform, I prefer Twitter as it has a more active research community.
You can briefly describe the idea, approach, and key results using Twitter threads (Figure 3) and use trending hashtags (e.g., #CVPR2022, #ICLR2022, etc.) to increase the reach. You can point to the arXiv/Github/project page links and cross-reference any authors/lab handle in the post.

Blogs are another way of publicizing your research. They are beneficial for those looking to understand the core idea easily without taking the headache of reading the complete paper. You can use freely available platforms like Medium, WordPress, and personal websites to publish and share your research if you are interested. To target the right audience, you can also try other popular platforms (e.g., PyImageSearch, Weights & Biases, Paperspace, Neptune AI, etc.).
Patents
If you are a researcher working on a product or use case, your work likely has a potential business value and real-life application. In such a case, it’s a good idea to file a patent for the invention to protect intellectual property (Figure 4). However, you should avoid disclosing the invention to the public (social media) in any form (like arXiv, codebase, etc.) that can be used to mimic the invention unless a patent has been filed for the same.
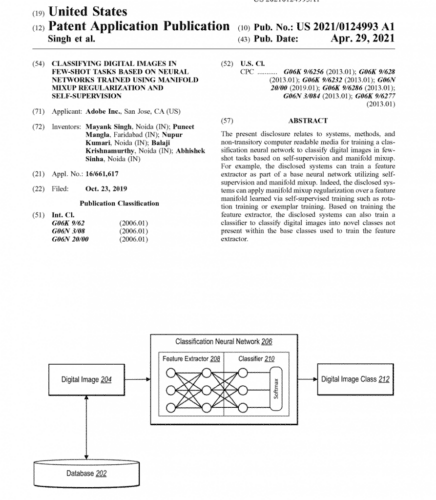
Many companies encourage and provide incentives to their employees for filing patent applications. And if you are a member of such an organization, you should take the opportunity to improve the credibility of your work.
Submitting to Workshops and Journals
These days, every conference organizes several workshops which focus and target a particular research area in Artificial Intelligence. Hence, by having your paper in workshops, you can target a concentrated audience. Most of these workshops allow papers to be submitted which are non-archival (i.e., are not included in any workshop proceedings). They usually consist of poster sessions, talks by researchers who closely work on that specific research topic, panels, and mentoring sessions.
Since these workshops are announced just after the conference decisions are out, you might need to act fast. Once you have identified a workshop relevant to your work, you just need to shorten and adjust the paper to workshop requirements.
Journals offer an excellent way to extend and bring more credibility to your work. If you think you can add more material to your research (analysis, experiments), you can submit an extended version to a journal. They accept papers throughout the year, and hence you can take your time to extend the research.
Preparing Poster and Video
Along with the camera-ready version, conferences ask authors to prepare a poster and video of the work. The deadline for this is much later than the camera-ready deadline, usually closer to the conference date. Carefully follow the poster requirements: dimensions, paper quality (for onsite conferences), orientation, etc. Add your institute/lab logo, email ids of all authors, and a QR code referring to your Github code/project page/arXiv landing page (Figure 5). Many attendees take pictures of posters and QR codes for future reference.
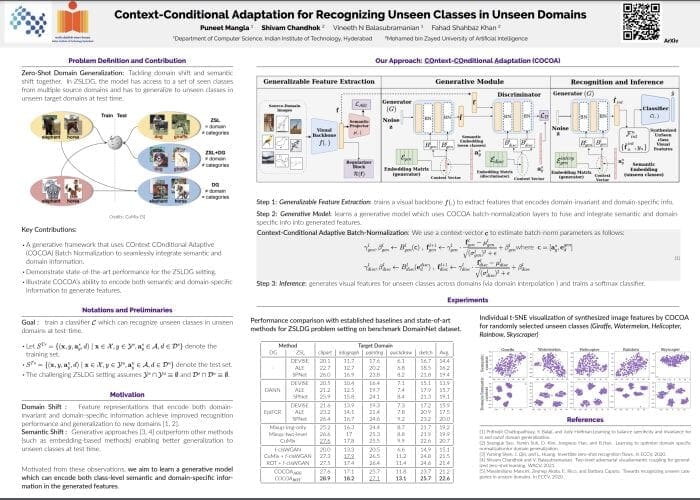
Avoid too much text. Instead, include as many figures, tables, and visualizations as possible. You can browse Overleaf for poster templates.
If preparing a video, ensure that you follow the same resolution, format, encoding, etc., as mentioned on the conference website. Script your video within the stipulated time for a smooth video. Once the poster and video are done, upload the same on your project page and YouTube channel.
Attending the Conference
Attending and presenting your work at the conference is perhaps the best part and advantage of getting your paper accepted (Figure 6). Use this opportunity to meet new people, and discuss with them. Stop by poster sessions to discuss and hear from the authors themselves. Make time to go around industry booths where you can find plenty of opportunities for job offers, internships, collaboration opportunities, and goodies.
An important thing to consider if planning to attend the conference is applying and looking for travel grants. If you have a paper accepted in an A* conference, most likely, you will receive a travel grant. Below are some travel grant opportunities.
- Conference Travel Grant: Every conference has its travel grants. Please actively scout the conference website and apply. Generally, a student first-author gets this grant most often.
- Google Travel Grant
- Microsoft Research India Travel Grants: If the link is down, email Satish Sangameswaran <satishsa@microsoft.com> and ask how to apply.
- Conference volunteer: Every conference provides free registration to an author that volunteers for a session or two at the conference. This is a great way to network and meet other peers. Please actively scout the conference website and apply.
- ACM India-IARCS Travel Grants
- Tata Trust
- If you are not selected in any of the above programs, ask your university or company if they can provide you with partial funding for your travel expenses.
Read the following blog post to learn about other sources of funding.
General Tips
I want to share a few more tips I have used in the past to gather research experience and skills.
Reviewing for Conferences
Reviewing papers for a conference is one of the quickest ways to develop self-critiquing ability (Figure 7). Critiquing papers from a reviewer’s point of view also helps you do the same for your paper. This allows you to identify potential concerns beforehand and write better papers.

Other benefits of reviewing are:
- Reading the latest research and learning about new directions before anyone else.
- Obtaining visibility in the research community as some conferences highlight names of outstanding reviewers in their proceedings or on their websites.
- Adding this to your CV can be very useful, especially for ones aiming to work in academia or apply for higher studies.
There are several ways through which one can serve as a conference reviewer.
- If your advisor has been serving as reviewer or area chair for any conferences, you can review the papers on his behalf by acting as a sub or external reviewer.
- Some conferences request the authors to serve as reviewers. If you have submitted your work to any conference, you should check for such an opportunity.
- Sometimes conferences advertise on Twitter or their website that they need reviewers. You can also explicitly reach out to the area and program chairs on Twitter or email and inform them of your availability as a reviewer.
Summer Schools
Summer schools are events organized by universities or companies held over 3-14 days. They offer beginners and young researchers the perfect opportunity to dive deep into their areas of interest and learn from experienced researchers. They consist of activities like poster sessions (where you can present your published or ongoing project), breakout sessions, panel sessions, talks, hands-on sessions, etc. These aim to bring together young and experienced researchers to interact, learn, and share their experiences.
The best part is that most of these summer schools don’t require you to have any pre-requisite knowledge of Machine Learning or Deep Learning (some Math with programming experience is more than sufficient). They also have scholarship programs to partially or fully fund the registration and travel expenses. To be considered for scholarships, you need to have a strong profile.
Here are some of the popular Machine Learning Summer Schools that are organized every year.
- Eastern European Machine Learning (EEML) Summer School is a week-long school around core topics regarding machine learning and artificial intelligence topics, including lectures and hands-on sessions. The school is organized by DeepMind (a pioneer in AI research).
- Summer School of Machine Learning at Skoltech (SMILES) is a one-week online intensive course about modern statistical machine learning methods. It aims at bringing together the Machine Learning community from the CIS, Central Asia, and the Caucasus regions (Figure 8).
- Summer School on Computer Vision and Machine Learning by IIIT Hyderabad deals with the basics of machine learning or the application of classic machine learning in computer vision, image processing, biometrics, and the latest advancements in machine learning.
- CIFAR hosts the Deep Learning + Reinforcement Learning (DLRL) Summer School in partnership with Canada’s three national AI institutes: Amii in Edmonton, Mila in Montreal, and the Vector Institute in Toronto. It covers the foundational research, new developments, and real-world applications of deep learning and reinforcement learning.

You can refer to the complete list of summer schools in the following GitHub compilation.
Research Programs
Research programs like internships, fellowships, residency, and pre-doctoral programs offer one of the best ways to work with experienced researchers and gather experience while getting paid a handsome stipend. Getting into one of these programs provides you an edge while applying for higher studies (Masters or Ph.D.) or full-time research roles.
Internships are 3- to 6-month programs and can be industrial and academic. Tech giants (e.g., Google, Microsoft, Amazon, Adobe, Uber, and Apple) hire undergraduates, graduates, and PhDs worldwide for their prestigious summer internship programs. Academic institutions (e.g., UC Berkeley, IITs, Stanford, and CMU) also have similar research programs where you will be working with their professors.
Fellowships and AI residency programs are 1- to 2-year research training programs where you can work on cutting-edge research, publish papers, and file patents. Companies like Google, Microsoft (Figure 9), Uber, and Apple hire every year for their research fellowship or AI residency programs. A complete list of these programs can be found at https://github.com/dangkhoasdc/awesome-ai-residency.

Keep yourself updated on platforms like Linkedin, Twitter, and career pages to know more about the applications for these programs.
What's next? We recommend PyImageSearch University.
86+ total classes • 115+ hours hours of on-demand code walkthrough videos • Last updated: March 2026
★★★★★ 4.84 (128 Ratings) • 16,000+ Students Enrolled
I strongly believe that if you had the right teacher you could master computer vision and deep learning.
Do you think learning computer vision and deep learning has to be time-consuming, overwhelming, and complicated? Or has to involve complex mathematics and equations? Or requires a degree in computer science?
That’s not the case.
All you need to master computer vision and deep learning is for someone to explain things to you in simple, intuitive terms. And that’s exactly what I do. My mission is to change education and how complex Artificial Intelligence topics are taught.
If you're serious about learning computer vision, your next stop should be PyImageSearch University, the most comprehensive computer vision, deep learning, and OpenCV course online today. Here you’ll learn how to successfully and confidently apply computer vision to your work, research, and projects. Join me in computer vision mastery.
Inside PyImageSearch University you'll find:
- ✓ 86+ courses on essential computer vision, deep learning, and OpenCV topics
- ✓ 86 Certificates of Completion
- ✓ 115+ hours hours of on-demand video
- ✓ Brand new courses released regularly, ensuring you can keep up with state-of-the-art techniques
- ✓ Pre-configured Jupyter Notebooks in Google Colab
- ✓ Run all code examples in your web browser — works on Windows, macOS, and Linux (no dev environment configuration required!)
- ✓ Access to centralized code repos for all 540+ tutorials on PyImageSearch
- ✓ Easy one-click downloads for code, datasets, pre-trained models, etc.
- ✓ Access on mobile, laptop, desktop, etc.
Summary
Visible research receives more citations and provides better opportunities to its authors. Thus, it is important to spend concentrated time and effort to improve the visibility of your research after acceptance.
The first thing to do as soon as your paper is accepted is to prepare a camera-ready version. Since the feedback is fresh in your mind, it can be incorporated easily. Be sure to add acknowledgments at the end of the paper and use the opportunity to thank funding sources, fellowship sources, and labmates who helped with the paper and could not be included as co-authors.
Upload the camera-ready version to arXiv and the codebase to GitHub. Ensure that the ReadME.md mentions the instructions to set up the environment and dataset and run training and inference scripts. Additionally, you can have a project page that summarizes the work’s main idea with sample results and links to the arXiv page and code.
Announce your research on social media platforms like Twitter and LinkedIn. Use trending conference hashtags and tag your co-authors to increase the reach. Write and share blog posts as they are beneficial for those looking to understand the core idea easily without taking the time to read the complete paper.
File patents, submit to workshops, and extend your work to journals. This will further improve the credibility of your research. While preparing posters and videos, ensure that you meet the conference requirements. Have a QR code that links to your arXiv, GitHub, or project page. If planning to attend the conference, consider applying to Conference, Microsoft, Google, ACM, etc., travel grants.
To gather research experience and skills, review conference papers, participate in summer schools, and apply for research internship and fellowship programs.
I hope this lesson helps you improve the visibility of your research after acceptance. This concludes the series on How to Publish Novel Research. Thanks for sticking through the end, and stay tuned for another new series.
Citation Information
Mangla, P. “Ensuring Your Research Stays Visible and General Tips,” PyImageSearch, P. Chugh, R. Raha, K. Kudriavtseva, and S. Huot, eds., 2022, https://pyimg.co/kfguv
@incollection{Mangla_2022_Ensuring_Research,
author = {Puneet Mangla},
title = {Ensuring Your Research Stays Visible and General Tips},
booktitle = {PyImageSearch},
editor = {Puneet Chugh and Ritwik Raha and Kseniia Kudriavtseva and Susan Huot},
year = {2022},
note = {https://pyimg.co/kfguv},
}

Unleash the potential of computer vision with Roboflow - Free!
- Step into the realm of the future by signing up or logging into your Roboflow account. Unlock a wealth of innovative dataset libraries and revolutionize your computer vision operations.
- Jumpstart your journey by choosing from our broad array of datasets, or benefit from PyimageSearch’s comprehensive library, crafted to cater to a wide range of requirements.
- Transfer your data to Roboflow in any of the 40+ compatible formats. Leverage cutting-edge model architectures for training, and deploy seamlessly across diverse platforms, including API, NVIDIA, browser, iOS, and beyond. Integrate our platform effortlessly with your applications or your favorite third-party tools.
- Equip yourself with the ability to train a potent computer vision model in a mere afternoon. With a few images, you can import data from any source via API, annotate images using our superior cloud-hosted tool, kickstart model training with a single click, and deploy the model via a hosted API endpoint. Tailor your process by opting for a code-centric approach, leveraging our intuitive, cloud-based UI, or combining both to fit your unique needs.
- Embark on your journey today with absolutely no credit card required. Step into the future with Roboflow.
Join the PyImageSearch Newsletter and Grab My FREE 17-page Resource Guide PDF
Enter your email address below to join the PyImageSearch Newsletter and download my FREE 17-page Resource Guide PDF on Computer Vision, OpenCV, and Deep Learning.

Comment section
Hey, Adrian Rosebrock here, author and creator of PyImageSearch. While I love hearing from readers, a couple years ago I made the tough decision to no longer offer 1:1 help over blog post comments.
At the time I was receiving 200+ emails per day and another 100+ blog post comments. I simply did not have the time to moderate and respond to them all, and the sheer volume of requests was taking a toll on me.
Instead, my goal is to do the most good for the computer vision, deep learning, and OpenCV community at large by focusing my time on authoring high-quality blog posts, tutorials, and books/courses.
If you need help learning computer vision and deep learning, I suggest you refer to my full catalog of books and courses — they have helped tens of thousands of developers, students, and researchers just like yourself learn Computer Vision, Deep Learning, and OpenCV.
Click here to browse my full catalog.