In today’s blog post we will investigate a practical use case of applying deep learning to hydroponics, a type of method used to grow plants without soil using mineral-rich nutrient solutions in a water solvent.
Specifically, you will learn how to train a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) using Keras to automatically classify root health without having to physically touch the plants.
The actual experiment design of this tutorial is motivated by Darrah et al. in their 2017 paper, Real- time Root Monitoring of Hydroponic Crop Plants: Proof of Concept for a New Image Analysis System.
Such a system can improve the yields of existing hydroponic farms making farms more efficient and sustainable to run. Of course, the successful application of hydroponics has massive implications for the medical marijuana industry.
While potentially controversial, and knowing full well that I’m going to get a few angry/upset emails about this blog post, I decided to post today’s tutorial anyway.
It’s important, useful, and highly educational for us as students, researchers, and engineers to see practical examples of how deep learning can and is being applied in the real-world.
Furthermore, today’s tutorial is not meant to be a discussion on the legality, morality, or usage of marijuana — this is not a platform to share “Legalize It” or NORML campaigns, anti-drug campaigns, or simply have a discussion on the recreational use of marijuana. There are more than enough websites on the internet to do that already, and if you feel the need to have such a discussion please do, just understand that PyImageSearch is not that platform.
I’d also urge you to keep in mind that we’re all researchers, students, and developers here, and most importantly, we’re all here to learn from practical, real-world examples. Be civil, regardless of whether you agree or disagree with some of the downstream implications of hydroponics.
With all that said, to learn more about how deep learning is being applied to hydroponics (and yes, medical marijuana), just keep reading!
Deep learning, hydroponics, and medical marijuana
2020-06-15 Update: This blog post is now TensorFlow 2+ compatible!
In the first half of today’s blog post, we’ll briefly discuss the concept of hydroponic farms, the relation they have to marijuana, and how deep learning intersects them both.
From there we’ll implement a Convolutional Neural Network with Keras to automatically classify root health of plants grown in a hydroponic system without having to physically touch or interfere with the plant.
Finally, we’ll review the results of our experiment.
What is hydroponics?

Hydroponics is a massive industry with an estimated market value of $21,203.5 million USD (yes, million) in 2016. The market is expected to grow at a 6.5% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) year over year from 2018 to 2023. Europe and Asia are expected to grow at similar rates as well (source for all statistics).
Hydroponics itself is a subset of hydroculture, the process of growing plants without utilizing soil and instead using mineral-rich solutions in a water solvent.
Using hydroponic methods, plants can grow with only their roots touching the mineral solution.
If you automatically correlate the term “hydroponics” with “marijuana”, keep in mind that hydroponic farming has been endorsed and used by major governments and organizations, including the United States, NASA, Europe and even the fabled Hanging Gardens of Babylon.
A great example is the International Space Station (ISS) — we’ve had hydroponic experiments, including growing vegetables, going on at the ISS for years.
Hydroponics is a science that has existed since the Babylonians and Aztecs, and continues to be used in modern times — so before you turn your nose up, keep in mind that this is actual science, and a science far older than computer vision and deep learning.
So, why bother with hydroponic farming at all?
Nutrient soil continues to come at a premium, especially due to irresponsible or over-farming of land, disease, war, deforestation, and an ever-changing environment just to name a few.
Hydroponic farms allow us to grow our fruits and veggies in smaller areas where traditional soil farms may be impossible.
And if you want to consider an even bigger picture, hydroponics will undoubtedly be utilized if we were to ever colonize Mars.
What does hydroponics have to do with medical marijuana?

If you read the previous section on what hydroponics is and why we use the method, it should come as no surprise that hydroponics is widely used in the marijuana industry, even before legalization legislation (in some states) in the United States.
I’m not going to provide an exhaustive review of hydroponics and medical marijuana (for that, you can refer to this article), but the gist is that:
- Prior to the legalization of marijuana (in some states of the United States), growers would want to keep their plants secret and safe — growing indoors hydroponically helped with this problem.
- Medical marijuana rules are new in the United States and in some cases, the only allowed method to grow is hydroponically.
- Growing hydroponically can help conserve our valuable soil which can take decades or more to naturally replenish itself.
According to reports from the Brightfield Group, the cannabis market was valued at $7.7 billion back in 2017 with a Compound Annual Growth Rate as high as 60% percent as other countries and states legalize — this adds up to a market valuation of $31.4 billion come 2021 (source).
There is a lot of money in hydroponics and marijuana, and in a high-risk, high-reward industry that is inherently dependent on (1) legislation and (2) technology, deep learning has found yet another application.
How do deep learning, computer vision, and hydroponics intersect?
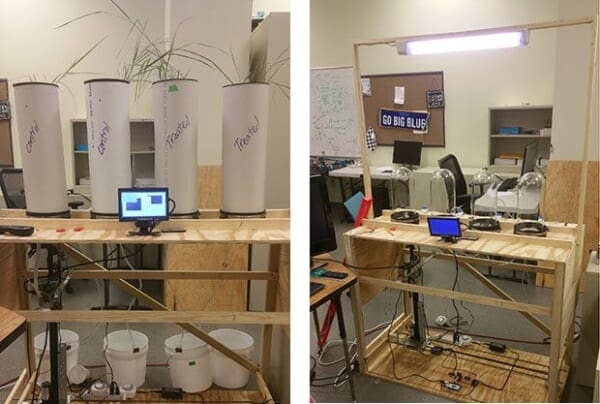

Back in 2017, PyImageSearch reader Timothy Darrah, an undergraduate at Tennessee State University, reached out to me with an interesting problem — he needed to devise an algorithm to automatically classify plant roots without being able to touch or interfere with the plants in anyway.
In particular, Darrah was working with switchgrass plants, a dominant species of North American prairie grass.
Note: Darrah et al.’s work was published in a paper entitled Real- time Root Monitoring of Hydroponic Crop Plants: Proof of Concept for a New Image Analysis System. Darrah has graciously allowed me to host his paper for your viewing.
The overall goal of the project was to develop an automated root growth analysis system capable of accurately measuring the roots followed by detecting any growth problems:
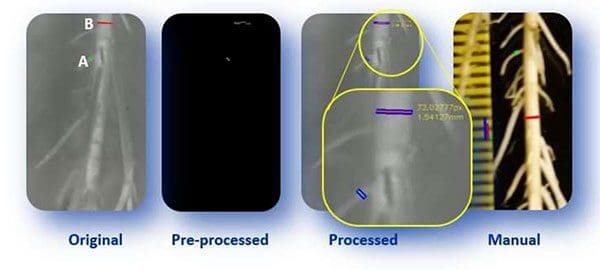
In particular, roots needed to be classified into two groups:
- “Hairy” roots
- “Non-hairy” roots
The “hairier” a root is, the better the root can suck up nutrients.
The “less hairy” the root is, the fewer nutrients it can intake, potentially leading to the plant starving and dying.
For this project, Timothy, along with Mahesh Rangu (a Ph.D. student) and their advisors, Dr. Erdem Erdemir and Dr. Suping Zhou, developed a system to automatically capture root images without having to disturb the plant itself.
Example images of their experimental setup can be seen in Figure 3 at the top of this section.
From there, they needed to apply computer vision to classify the root into one of the two categories (and eventually multiple categories for detecting other root afflictions).
The only question was how to solve the image classification problem?
Note: Timothy and the rest of the team solved their initial problem after Timothy emailed me in April 2017 asking for an algorithm to try. I suggested Local Binary Patterns which worked for them; however, for the sake of this tutorial, we’ll explore how deep learning can be utilized as well.
Our image dataset
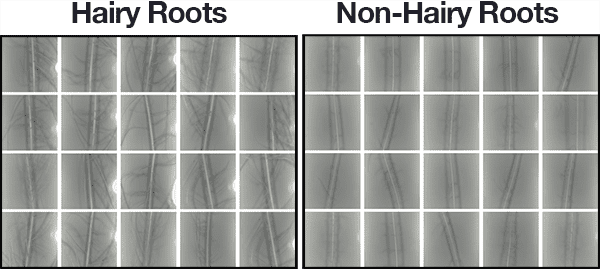
Our dataset of 1,524 root images includes:
- Hairy: 748 images (left)
- Non-hairy: 776 images (right)
A subset of the example images for each class can be seen in Figure 4 above.
The original images were captured at a higher resolution of 1920×1080 pixels; however, for the sake for this blog post, I’ve resized them to 256×256 pixels as a matter of convenience (and to save space/bandwidth).
The resizing was performed by:
- Resizing the height to 256 pixels
- And then taking the center 256-pixel crop
Since the center of the image always contained the mass of root hairs (or lack thereof), this resizing and cropping method worked quite well.
Darrah et al. have graciously allowed us to use these images for our own education as well (but you cannot use them for commercial purposes).
In the remainder of this tutorial, you will learn how to train a deep learning network to automatically classify each of these root species classes.
Configuring your development environment
To configure your system for this tutorial, I recommend following either of these tutorials:
Either tutorial will help you configure your system with all the necessary software for this blog post in a convenient Python virtual environment.
Please note that PyImageSearch does not recommend or support Windows for CV/DL projects.
Project structure
To review the project structure directly in your terminal, first, grab the “Downloads” for this post and unzip the archive.
Then navigate into the project directory and use the tree command to examine the contents:
$ tree --dirsfirst --filelimit 10 . ├── dataset │ ├── hairy_root [748 images] │ └── non_hairy_root [776 images] ├── pyimagesearch │ ├── __init__.py │ └── simplenet.py ├── train_network.py └── plot.png 4 directories, 4 files
Our dataset/ directory consists of hairy_root/ and non_hairy_root/ images.
The pyimagesearch/ directory is a Python module containing simplenet.py . The SimpleNet architecture is a Keras deep learning architecture I designed for root health classification. We’ll be reviewing this architecture today.
We’ll then train our network with train_network.py , producing plot.png , our training plot. We’ll walk through the training script line by line so you have an understanding of how it works.
Let’s begin!
Utilizing deep learning to classify root health
Now that we have an understanding of both (1) hydroponics and (2) the dataset we are working with, we can get started.
Implementing our Convolutional Neural Network
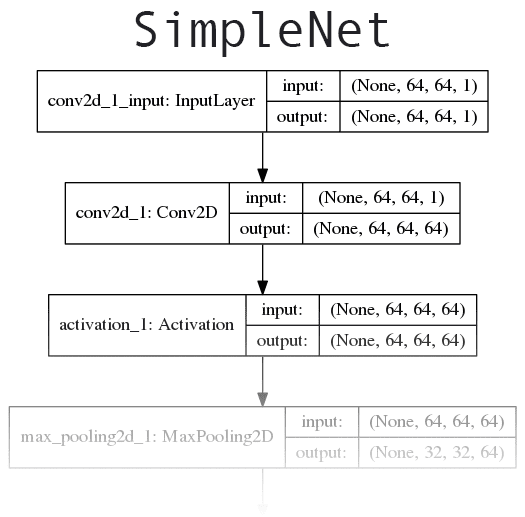
The network we’ll be implementing today is loosely based on concepts introduced in AlexNet and OverFeat.
Our network will start off with convolutional filters with a larger filter size used to quickly reduce the spatial dimensions of the volume. From there we’ll apply two CONV layers used to learn 3×3 filters. Click here to see the full network architecture diagram.
Open up the simplenet.py file and insert the following code:
# import the necessary packages from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D from tensorflow.keras.layers import MaxPooling2D from tensorflow.keras.layers import Activation from tensorflow.keras.layers import Flatten from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
We begin our script by importing necessary layer types from keras . Scroll down to see each in use.
We also import the keras backend . The backend will allow us to dynamically handle different input shapes in the next block where we define the SimpleNet class and build method:
class SimpleNet: @staticmethod def build(width, height, depth, classes, reg): # initialize the model along with the input shape to be # "channels last" model = Sequential() inputShape = (height, width, depth) # if we are using "channels first", update the input shape if K.image_data_format() == "channels_first": inputShape = (depth, height, width)
The SimpleNet class definition begins on Line 11.
Our only method, build , is defined on Line 13.
The first step in the function is to initialize a Sequential model (Line 16).
Then we specify our inputShape where input images are assumed to be 64×64 pixels in size (Line 17).
Most people will be using TensorFlow as the backend which assumes "channels_last" last ordering. In case you are using Theano or another "channels_first" backend, then the inputShape is modified on Lines 20 and 21.
Let’s begin adding layers to our network:
# first set of CONV => RELU => POOL layers
model.add(Conv2D(64, (11, 11), input_shape=inputShape,
padding="same", kernel_regularizer=reg))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# second set of CONV => RELU => POOL layers
model.add(Conv2D(128, (5, 5), padding="same",
kernel_regularizer=reg))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# third (and final) CONV => RELU => POOL layers
model.add(Conv2D(256, (3, 3), padding="same",
kernel_regularizer=reg))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
The first CONV => RELU => POOL block of layers (Lines 24-28) uses a larger filter size to (1) help detect larger groups of hairs (or lack thereof), followed by (2) quickly reducing the spatial dimensions of the volume.
We learn more filters per CONV layer the deeper in the network we go (Lines 31-42).
Standard Rectified Linear Unit (RELU) activation is utilized throughout. Alternatives and tradeoffs are discussed in my deep learning book.
POOL layers have a primary function of progressively reducing the spatial size (i.e. width and height) of the input volume to a layer. You’ll commonly see POOL layers between consecutive CONV layers in a CNN such as this example.
In each of the blocks above, we dropout 25% of the nodes (disconnect random neurons) in an effort to introduce regularization and help the network generalize better. This method is proven to reduce overfitting, increase accuracy, and allow our network to generalize better for unfamiliar images.
Our last FC => RELU block ends with a softmax classifier:
# first and only set of FC => RELU layers
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(512, kernel_regularizer=reg))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
# softmax classifier
model.add(Dense(classes))
model.add(Activation("softmax"))
# return the constructed network architecture
return model
Fully connected layers (Dense ) are common towards the end of CNNs. This time we apply 50% dropout.
Our softmax classifier is applied to our last fully connected layer which has 2 outputs corresponding to our two classes : (1) non_hairy_root , and (2) hairy_root .
Finally, we return the constructed model.
Implementing the driver script
Now that we’ve implemented SimpleNet , let’s create the driver script responsible for training our network.
Open up train_network.py and insert the following code:
# set the matplotlib backend so figures can be saved in the background
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use("Agg")
# import the necessary packages
from pyimagesearch.simplenet import SimpleNet
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.regularizers import l2
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from imutils import build_montages
from imutils import paths
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import argparse
import cv2
import os
Our driver script has a number of important imports. Let’s review them:
matplotlib: The de facto plotting package for Python. We’ll be plotting our training accuracy/loss data over time.SimpleNet: We defined this CNN architecture in the previous section.LabelEncoder: The scikit-learn package has a handy label encoder. We’ll perform “one-hot” encoding — more on that later.train_test_split: We’re going to segment our training data into a certain percentage of images for training and the remaining images for testing. Splitting data is common in machine learning and you’ll find a similar function no matter what tool you are using.classification_report: Allows us to conveniently print statistics in a readable format in our terminal.Adam: A learning optimizer that we’ll be using. Another option would have been SGD.l2: Incorporated into the loss function, the l2 regularizer allows us to penalize layer parameters or layer activity during optimization. This will prevent overfitting and allow our network to generalize.build_montages: We’ll view the results of our hard work in a montage of images within one frame. This comes from my imutils package.paths: Also from imutils, this function will extract all image paths (recursively) from an input directory.argparse: For parsing command line arguments — we’ll review this next.cv2: Don’t forget about OpenCV! We’ll use OpenCV for preprocessing as well as visualization/display.os: I’m not a Windows guy, nor do I officially support Windows here on PyImageSearch, but we’ll useos.path.sepwhich will accommodate Windows and Linux/Mac path separators.
That was a mouthful. The more you work in the field of CV and DL, the more familiar you’ll become with these and other packages and modules.
Let’s take advantage of one of them. We’ll use argparse to parse our command line arguments:
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-d", "--dataset", required=True,
help="path to input dataset")
ap.add_argument("-e", "--epochs", type=int, default=100,
help="# of epochs to train our network for")
ap.add_argument("-p", "--plot", type=str, default="plot.png",
help="path to output loss/accuracy plot")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
Readers of my blog tend to be familiar with these lines of code, but I always explain them for newcomers. The argparse tool will parse a command string entered in your terminal with command line arguments. Be sure to read my post on Python, argparse, and command line arguments if it is your first time here or if you’ve never used command line arguments before.
We have three command line arguments for our driver script:
--dataset: This is the path to our dataset of images. This argument is required as we need data for training.--epochs: You can experiment with training for different numbers of iterations (epochs). I found100to be adequate, so it is the default.--plot: If you’d like to specify a path + filename for your plot, you can do so with this argument. By default, your plot will be named"plot.png"and saved in the current working directory. Each time you run an experiment with a goal of better performance, you should make note of DL parameters and also name your plot so you’ll remember which experiment it corresponds to.
Now that we’ve parsed our command line arguments, let’s load + preprocess our image data and parse labels:
# grab the list of images in our dataset directory, then initialize
# the list of data (i.e., images) and class images
print("[INFO] loading images...")
imagePaths = list(paths.list_images(args["dataset"]))
data = []
labels = []
# loop over the image paths
for imagePath in imagePaths:
# extract the class label from the filename
label = imagePath.split(os.path.sep)[-2]
# load the image, convert it to grayscale, and resize it to be a
# fixed 64x64 pixels, ignoring aspect ratio
image = cv2.imread(imagePath)
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
image = cv2.resize(image, (64, 64))
# update the data and labels lists, respectively
data.append(image)
labels.append(label)
On Line 34 we create a list of all imagePaths in our dataset. We then go ahead and initialize a place to hold our data in memory as well as our corresponding labels (Lines 35 and 36).
Given our imagePaths , we proceed to loop over them on Line 39.
The first step in the loop is to extract our class label on Line 41. Let’s see how this works in a Python Shell:
$ python
>>> from imutils import paths
>>> import os
>>> imagePaths = list(paths.list_images("dataset"))
>>> imagePath = imagePaths[0]
>>> imagePath
'dataset/hairy_root/100_a.jpg'
>>> imagePath.split(os.path.sep)
['dataset', 'hairy_root', '100_a.jpg']
>>> imagePath.split(os.path.sep)[-2]
'hairy_root'
>>>
Notice how by using imagePath.split and providing the split character (the OS path separator — “/” on Unix and “\” on Windows), the function produces a list of folder/file names (strings) which walk down the directory tree (Lines 8 and 9). We grab the second-to-last index, the class label, which in this case is 'hairy_root' (Lines 10 and 11).
Then we proceed to load the image and preprocess it (Lines 45-47). Grayscale (single channel) is all we need to identify hairy or non-hairy roots. Our network requires 64×64 pixel images by design.
Finally, we add the image to data and the label to labels (Lines 50 and 51).
Next, we’ll reshape our data and encode labels:
# convert the data into a NumPy array, then preprocess it by scaling # all pixel intensities to the range [0, 1] data = np.array(data, dtype="float") / 255.0 # reshape the data matrix so that it explicity includes a channel # dimension data = data.reshape((data.shape[0], data.shape[1], data.shape[2], 1)) # encode the labels (which are currently strings) as integers le = LabelEncoder() labels = le.fit_transform(labels) # transform the labels into vectors in the range [0, classes], # generating a vector for each label, where the index of the label # is set to '1' and all other entries are set to '0' -- this process # is called "one-hot encoding" labels = to_categorical(labels, 2) # partition the data into training and testing splits using 60% of # the data for training and the remaining 40% for testing (trainX, testX, trainY, testY) = train_test_split(data, labels, test_size=0.40, stratify=labels, random_state=42)
Data is reshaped on Lines 55-59. During the process, we convert from a list to a NumPy array of floats that are scaled to [0, 1]. We also add the channel dimension even though we have only one grayscale channel. This extra dimension is expected by our CNN.
We then encode our labels on Lines 62-69. We use “one-hot encoding” which implies that we have a vector where only one of the elements (classes) is “hot” at any given time. Review my recent Keras tutorial for an example applied to a dataset of 3 classes to grasp the concept.
Now comes the splitting of the data. I’ve reserved 60% of our data for training and 40% for testing (Lines 73 and 74).
Let’s compile our model:
# initialize the optimizer and model
print("[INFO] compiling model...")
opt = Adam(lr=1e-4, decay=1e-4 / args["epochs"])
model = SimpleNet.build(width=64, height=64, depth=1,
classes=len(le.classes_), reg=l2(0.0002))
model.compile(loss="binary_crossentropy", optimizer=opt,
metrics=["accuracy"])
We initialize the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 1e-4 and learning rate decay (Line 78).
Note: The default learning rate for Adam is 1e-3 , but I found through experimentation that using 1e-3 was too high — the network was unable to gain any “traction” and unable to learn. Using 1e-4 as the initial learning rate allowed the network to start learning. This goes to show you how important it is to understand deep learning parameters and fundamentals. Grab a copy of my book, Deep Learning for Computer Vision with Python, to discover my best practices, tips, and suggestions when tuning these parameters.
I also included a small amount of regularization to help prevent overfitting and ensure the network generalizes. This regularization is shown on Lines 79 and 80 where we build our model while specifying our dimensions, encoded labels, as well as the regularization strength.
We compile our model on Lines 81 and 82. Since our network has only two classes, we use "binary_crossentropy" . If you have > 2 classes, you would want to use "categorical_crossentropy" .
Training is kicked off next, followed by evaluation:
# train the network
print("[INFO] training network for {} epochs...".format(
args["epochs"]))
H = model.fit(x=trainX, y=trainY, validation_data=(testX, testY),
batch_size=32, epochs=args["epochs"], verbose=1)
# evaluate the network
print("[INFO] evaluating network...")
predictions = model.predict(testX, batch_size=32)
print(classification_report(testY.argmax(axis=1),
predictions.argmax(axis=1), target_names=le.classes_))
Training, also known as “fitting a model” is kicked off on Lines 87 and 88. I’ve set a batch size of 32 .
We then evaluate the network and print a classification_report in the terminal (Lines 92-94).
Next, we use matplotlib to generate a training plot:
# plot the training loss and accuracy
N = args["epochs"]
plt.style.use("ggplot")
plt.figure()
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["loss"], label="train_loss")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["val_loss"], label="val_loss")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["accuracy"], label="train_acc")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["val_accuracy"], label="val_acc")
plt.title("Training Loss and Accuracy on Dataset")
plt.xlabel("Epoch #")
plt.ylabel("Loss/Accuracy")
plt.legend(loc="lower left")
plt.savefig(args["plot"])
2020-06-15 Update: In order for this plotting snippet to be TensorFlow 2+ compatible the H.history dictionary keys are updated to fully spell out “accuracy” sans “acc” (i.e., H.history["val_accuracy"] and H.history["accuracy"]). It is semi-confusing that “val” is not spelled out as “validation”; we have to learn to love and live with the API and always remember that it is a work in progress that many developers around the world contribute to.
The above is a good recipe to refer to for producing a training plot when working with Keras and deep learning. The code plots loss and accuracy on the same plot (y-axis) throughout the training period (x-axis).
We call savefig to export the plot image to disk (Line 108).
Finally, let’s visualize the output:
# randomly select a few testing images and then initialize the output
# set of images
idxs = np.arange(0, testY.shape[0])
idxs = np.random.choice(idxs, size=(25,), replace=False)
images = []
# loop over the testing indexes
for i in idxs:
# grab the current testing image and classify it
image = np.expand_dims(testX[i], axis=0)
preds = model.predict(image)
j = preds.argmax(axis=1)[0]
label = le.classes_[j]
# rescale the image into the range [0, 255] and then resize it so
# we can more easily visualize it
output = (image[0] * 255).astype("uint8")
output = np.dstack([output] * 3)
output = cv2.resize(output, (128, 128))
# draw the colored class label on the output image and add it to
# the set of output images
color = (0, 0, 255) if "non" in label else (0, 255, 0)
cv2.putText(output, label, (3, 20), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5,
color, 2)
images.append(output)
# create a montage using 128x128 "tiles" with 5 rows and 5 columns
montage = build_montages(images, (128, 128), (5, 5))[0]
# show the output montage
cv2.imshow("Output", montage)
cv2.waitKey(0)
Whenever you are testing a machine learning or deep learning model, you shouldn’t only rely on statistics as proof that the model is working. You should also visualize your results on test images. Sometimes I make a separate script which loads an arbitrary image and classifies + displays it. Given that these images are all similar, I opted to make a montage of images so we can visually check at a glance if our model is performing well.
The steps to do this include:
- Randomly select some testing image indexes to visualize (Lines 112 and 113). Also initialize a list to hold the
images(Line 114). - Loop over the random image
idxsbeginning on Line 117:- Load and classify the image (Lines 119-122). We take the index of the highest prediction and feed the index to our label encoder to generate a
label. - Rescale/resize the image for visualization (Lines 126-128).
- Draw the
labeltext on the output image (Lines 132-134). The hairy roots (good) will havegreenfont and non-hairy roots (bad) will be red. - Add the output image to our images list so that we can later build a montage (Line 135).
- Load and classify the image (Lines 119-122). We take the index of the highest prediction and feed the index to our label encoder to generate a
- Build a montage of the results (Line 138). Learn to build Montages with OpenCV.
Finally, we display the results until a key is pressed on the final two lines.
Root health classification results
To see how our root health deep neural network performed, be sure to use the “Downloads” section of this blog post to download the source code and dataset.
From there, open up a terminal, navigate to where you downloaded + extracted the code, and execute the following command:
$ python train_network.py --dataset dataset
Using TensorFlow backend.
[INFO] loading images...
[INFO] compiling model...
[INFO] training network for 100 epochs...
Epoch 1/100
29/29 [==============================] - 1s 23ms/step - loss: 0.9461 - accuracy: 0.4956 - val_loss: 0.9262 - val_accuracy: 0.5098
Epoch 2/100
29/29 [==============================] - 0s 14ms/step - loss: 0.9149 - accuracy: 0.5470 - val_loss: 0.9097 - val_accuracy: 0.4902
Epoch 3/100
29/29 [==============================] - 0s 15ms/step - loss: 0.9045 - accuracy: 0.5208 - val_loss: 0.8931 - val_accuracy: 0.5098
...
Epoch 98/100
29/29 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.1081 - accuracy: 0.9891 - val_loss: 0.1360 - val_accuracy: 0.9770
Epoch 99/100
29/29 [==============================] - 0s 13ms/step - loss: 0.2083 - accuracy: 0.9551 - val_loss: 0.1358 - val_accuracy: 0.9852
Epoch 100/100
29/29 [==============================] - 0s 16ms/step - loss: 0.2043 - accuracy: 0.9420 - val_loss: 0.1648 - val_accuracy: 0.9541
[INFO] evaluating network...
precision recall f1-score support
hairy_root 1.00 0.91 0.95 299
non_hairy_root 0.92 1.00 0.96 311
accuracy 0.95 610
macro avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 610
weighted avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 610
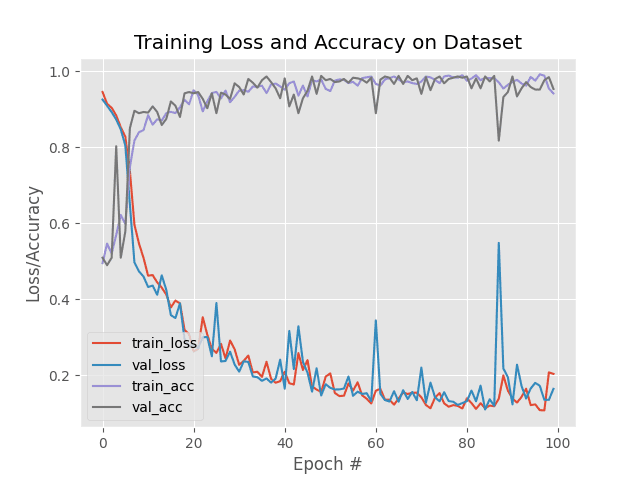
As we can see, our network obtained 95% classification accuracy, and as our plot demonstrates, there is no overfitting.
And furthermore, we can examine the montage of our results which again show that our network is accurately classifying each of the root types:
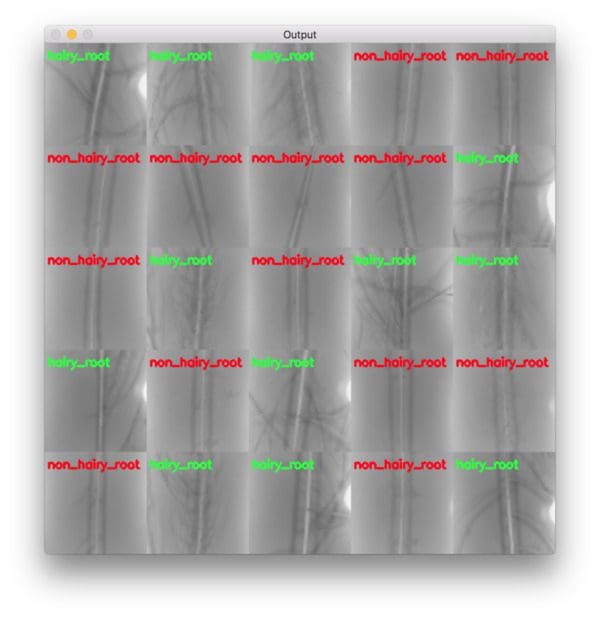
Using techniques such as this one, deep learning researchers, practitioners, and engineers can help solve real-world problems.
What's next? We recommend PyImageSearch University.
86+ total classes • 115+ hours hours of on-demand code walkthrough videos • Last updated: March 2026
★★★★★ 4.84 (128 Ratings) • 16,000+ Students Enrolled
I strongly believe that if you had the right teacher you could master computer vision and deep learning.
Do you think learning computer vision and deep learning has to be time-consuming, overwhelming, and complicated? Or has to involve complex mathematics and equations? Or requires a degree in computer science?
That’s not the case.
All you need to master computer vision and deep learning is for someone to explain things to you in simple, intuitive terms. And that’s exactly what I do. My mission is to change education and how complex Artificial Intelligence topics are taught.
If you're serious about learning computer vision, your next stop should be PyImageSearch University, the most comprehensive computer vision, deep learning, and OpenCV course online today. Here you’ll learn how to successfully and confidently apply computer vision to your work, research, and projects. Join me in computer vision mastery.
Inside PyImageSearch University you'll find:
- ✓ 86+ courses on essential computer vision, deep learning, and OpenCV topics
- ✓ 86 Certificates of Completion
- ✓ 115+ hours hours of on-demand video
- ✓ Brand new courses released regularly, ensuring you can keep up with state-of-the-art techniques
- ✓ Pre-configured Jupyter Notebooks in Google Colab
- ✓ Run all code examples in your web browser — works on Windows, macOS, and Linux (no dev environment configuration required!)
- ✓ Access to centralized code repos for all 540+ tutorials on PyImageSearch
- ✓ Easy one-click downloads for code, datasets, pre-trained models, etc.
- ✓ Access on mobile, laptop, desktop, etc.
Summary
In today’s blog post we explored a real-world application of deep learning: automatically classifying plant root health in hydroponic farms, and in particular, how such a system could be leveraged in the massively growing (no pun intended) medical marijuana industry.
In order to classify root health, we trained a Convolutional Neural Network with Keras and Python to label roots as “hairy” or “non-hairy”.
The more hairs a root has, the more easily it is able to intake nutrients. The fewer hairs a root has, the more it will struggle to suck up nutrients, potentially leading to the plant dying and the loss of the crop.
Using the method detailed in today’s post we were able to classify root health with over 95% accuracy.
For more information on how hydroponics and computer vision intersect, please refer to Darrah et al.’s 2017 publication.
I hope you enjoyed today’s blog post on applying deep learning to a real-world application.
To download the source code to this blog post (and signup for the PyImageSearch newsletter), just enter your email address in the form below!
Download the Source Code and FREE 17-page Resource Guide
Enter your email address below to get a .zip of the code and a FREE 17-page Resource Guide on Computer Vision, OpenCV, and Deep Learning. Inside you'll find my hand-picked tutorials, books, courses, and libraries to help you master CV and DL!


